가. 최근 보안 동향
- 최근 생성형 AI(*)인 클로드(*)를 활용한 해킹 공격 및 방어 사례가 증가하고 있다.
*생성형 AI(Generative AI, Gen AI): 기존 데이터를 학습하여 새로운 데이터(예: 글, 이미지, 음성 등)를 생성할 수 있는 인공지능 기술이다.
*클로드(Claude): 앤트로픽(Anthropic)에서 개발한 생성형 AI로, 프로그래밍(코딩)에 특화되어 있다.
Disrupting the first reported AI-orchestrated cyber espionage campaign
A report describing an a highly sophisticated AI-led cyberattack
www.anthropic.com
- 클로드를 보안 도구(예: Nmap, Burp Suite)와 연동하면 네트워크 스캔 결과를 자동으로 분석하고, 발견된 취약점에 대한 설명과 대응 방안을 보고서 형태로 제공받을 수 있다.
AI를 이용한 웹 모의해킹 방법(BurpSuite+Claude+MCP)
가. 용어 설명1. 생성형 AI 란?- 생성형 AI(Generative AI)는 기존 데이터를 학습하여 새로운 데이터(예: 글, 이미지, 음성 등)를 생성할 수 있는 인공지능 기술이다. 2. Claude 란?- 클로드(Claude)는 앤트로
hagsig.tistory.com
- 아래의 설치 가이드를 참고하여 클로드를 활용한 네트워크 스캔 방법을 학습해 보자.
나. AI 네트워크 스캔 환경 구축
1. Nmap 설치
- 엔맵(Nmap)은 네트워크를 스캔하고 분석하는 데 사용되는 오픈소스 유틸리티이다. 아래의 사이트에서 다운로드 및 설치한다.
Download the Free Nmap Security Scanner for Linux/Mac/Windows
Download Reference Guide Book Docs Zenmap GUI In the Movies Older versions (and sometimes newer test releases) are available from the Nmap release archive (and really old ones are in dist-old). For the more security-paranoid (smart) users, GPG detached sig
nmap.org
2. Python 및 MCP 서버 설치
2-1. Python 설치
- Nmap MCP Server(*) 설치를 위해서는 파이썬 3.10 이상의 버전을 설치하여야 한다. 아래의 사이트에서 다운로드 및 설치한다.
* MCP(Model Context Protocol): 생성형 AI가 긴 대화나 복잡한 내용을 더 잘 기억하고 처리할 수 있도록 도와주는 기술이다.
Download Python
The official home of the Python Programming Language
www.python.org
2-2. Nmap MCP Server 설치
- 아래의 명령어를 참고하여 Nmap MCP Server를 설치한다.
pip install mcp
- nmap-mcp-server 이름의 폴더를 생성한다.
mkdir C:\\Users\\hagsig\\nmap-mcp-server
- 생성한 폴더에 nmap-mcp-server.py 파일을 생성하고 아래의 내용을 추가하거나, 파일을 다운로드한다.
# nmap-mcp-server.py 소스코드
import asyncio
import json
import subprocess
from typing import Any, Optional
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from mcp.server import Server
from mcp.types import Tool, TextContent, ImageContent, EmbeddedResource
# MCP 서버 초기화
app = Server("nmap-server")
# 도구 목록 정의
@app.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> list[Tool]:
"""Claude가 사용할 수 있는 nmap 도구 목록"""
return [
Tool(
name="nmap_port_scan",
description="대상 호스트의 포트를 스캔합니다. 기본적으로 상위 1000개 포트를 스캔합니다.",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"target": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 대상 (IP 주소 또는 도메인)"
},
"ports": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 포트 범위 (예: '80,443' or '1-1000')",
"default": ""
},
"scan_type": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["tcp", "syn", "udp"],
"description": "스캔 타입: tcp(연결 스캔), syn(SYN 스캔), udp(UDP 스캔)",
"default": "tcp"
}
},
"required": ["target"]
}
),
Tool(
name="nmap_service_detection",
description="열린 포트에서 실행 중인 서비스와 버전을 감지합니다.",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"target": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 대상"
},
"ports": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 포트 범위",
"default": ""
}
},
"required": ["target"]
}
),
Tool(
name="nmap_os_detection",
description="대상 시스템의 운영체제를 감지합니다. (관리자 권한 필요)",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"target": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 대상"
}
},
"required": ["target"]
}
),
Tool(
name="nmap_script_scan",
description="NSE(Nmap Scripting Engine) 스크립트를 실행합니다.",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"target": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 대상"
},
"script": {
"type": "string",
"description": "실행할 스크립트 (예: 'vuln', 'default', 'http-title')",
"default": "default"
},
"ports": {
"type": "string",
"description": "스캔할 포트",
"default": ""
}
},
"required": ["target"]
}
),
Tool(
name="nmap_ping_scan",
description="대상 호스트가 활성화되어 있는지 확인합니다 (포트 스캔 없음).",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"target": {
"type": "string",
"description": "확인할 대상 (단일 IP 또는 네트워크 범위)"
}
},
"required": ["target"]
}
)
]
def run_nmap_command(args: list[str], timeout: int = 300) -> dict:
"""nmap 명령을 실행하고 결과를 파싱"""
try:
# XML 출력 옵션 추가
full_args = ["nmap", "-oX", "-"] + args
result = subprocess.run(
full_args,
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=timeout,
check=False
)
if result.returncode != 0 and result.returncode != 1:
# nmap은 호스트가 다운되어도 returncode 1을 반환할 수 있음
return {
"success": False,
"error": result.stderr or "Unknown error",
"raw_output": result.stdout
}
# XML 파싱
if result.stdout:
return parse_nmap_xml(result.stdout)
else:
return {
"success": False,
"error": "No output from nmap",
"raw_output": result.stderr
}
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
return {
"success": False,
"error": f"Scan timed out after {timeout} seconds"
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"success": False,
"error": str(e)
}
def parse_nmap_xml(xml_output: str) -> dict:
"""nmap XML 출력을 파싱하여 구조화된 데이터로 변환"""
try:
root = ET.fromstring(xml_output)
result = {
"success": True,
"scan_info": {},
"hosts": []
}
# 스캔 정보
runstats = root.find("runstats")
if runstats is not None:
finished = runstats.find("finished")
if finished is not None:
result["scan_info"]["elapsed"] = finished.get("elapsed", "")
result["scan_info"]["summary"] = finished.get("summary", "")
# 호스트 정보
for host in root.findall("host"):
host_info = {
"status": host.find("status").get("state") if host.find("status") is not None else "unknown",
"addresses": [],
"hostnames": [],
"ports": [],
"os": {}
}
# IP 주소
for addr in host.findall("address"):
host_info["addresses"].append({
"addr": addr.get("addr"),
"type": addr.get("addrtype")
})
# 호스트명
hostnames = host.find("hostnames")
if hostnames is not None:
for hostname in hostnames.findall("hostname"):
host_info["hostnames"].append({
"name": hostname.get("name"),
"type": hostname.get("type")
})
# 포트 정보
ports = host.find("ports")
if ports is not None:
for port in ports.findall("port"):
port_info = {
"port": port.get("portid"),
"protocol": port.get("protocol"),
"state": port.find("state").get("state") if port.find("state") is not None else "unknown",
"service": {}
}
service = port.find("service")
if service is not None:
port_info["service"] = {
"name": service.get("name", ""),
"product": service.get("product", ""),
"version": service.get("version", ""),
"extrainfo": service.get("extrainfo", "")
}
# 스크립트 결과
scripts = port.findall("script")
if scripts:
port_info["scripts"] = []
for script in scripts:
port_info["scripts"].append({
"id": script.get("id"),
"output": script.get("output")
})
host_info["ports"].append(port_info)
# OS 감지
os_elem = host.find("os")
if os_elem is not None:
osmatch = os_elem.find("osmatch")
if osmatch is not None:
host_info["os"] = {
"name": osmatch.get("name"),
"accuracy": osmatch.get("accuracy")
}
result["hosts"].append(host_info)
return result
except ET.ParseError as e:
return {
"success": False,
"error": f"XML parsing error: {str(e)}",
"raw_output": xml_output
}
@app.call_tool()
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: Any) -> list[TextContent]:
"""도구 호출 처리"""
if name == "nmap_port_scan":
target = arguments.get("target")
ports = arguments.get("ports", "")
scan_type = arguments.get("scan_type", "tcp")
args = []
if scan_type == "syn":
args.append("-sS")
elif scan_type == "udp":
args.append("-sU")
else:
args.append("-sT")
if ports:
args.extend(["-p", ports])
args.append(target)
result = run_nmap_command(args)
elif name == "nmap_service_detection":
target = arguments.get("target")
ports = arguments.get("ports", "")
args = ["-sV"]
if ports:
args.extend(["-p", ports])
args.append(target)
result = run_nmap_command(args)
elif name == "nmap_os_detection":
target = arguments.get("target")
args = ["-O", target]
result = run_nmap_command(args)
elif name == "nmap_script_scan":
target = arguments.get("target")
script = arguments.get("script", "default")
ports = arguments.get("ports", "")
args = ["--script", script]
if ports:
args.extend(["-p", ports])
args.append(target)
result = run_nmap_command(args, timeout=600)
elif name == "nmap_ping_scan":
target = arguments.get("target")
args = ["-sn", target]
result = run_nmap_command(args, timeout=60)
else:
result = {
"success": False,
"error": f"Unknown tool: {name}"
}
return [TextContent(
type="text",
text=json.dumps(result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
)]
async def main():
"""서버 실행"""
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await app.run(
read_stream,
write_stream,
app.create_initialization_options()
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
3. 클로드 설치 및 설정파일 수정
3-1. 클로드 데스크톱 설치
- 아래의 사이트에 접속하여 클로드 데스크톱 버전을 설치한다.
Download Claude
Download Claude for your desktop or mobile device.
www.claude.com
3-2. 클로드 설정파일 수정
- 클로드 데스크톱에서 MCP 서버를 사용하기 위해서는 claude_desktop_config.json 설정 파일의 수정이 필요하다.
- 운영체제(OS) 별 claude_desktop_config.json 파일의 경로는 아래와 같다.
# 운영체제(OS)별 claude_desktop_config.json 파일 경로
# macOS
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
# Windows
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
# Linux
~/.config/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
- claude_desktop_config.json 설정 파일에 아래의 내용을 추가한다.
{
"mcpServers": {
"nmap": {
"command": "python",
"args": [
"C:\\Users\\hagsig\\nmap-mcp-server\\nmap-mcp-server.py"
],
"env": {
"PYTHONUNBUFFERED": "1"
}
}
}
}
※ 만약 다른 MCP 서버와의 연결을 위해 추가된 내용이 있을 경우 아래와 같이 내용을 추가한다.
{
"mcpServers": {
"burp": {
"command": "c:\\users\\hagsig\\appdata\\local\\programs\\burpsuitecommunity\\jre\\bin\\java.exe",
"args": [
"-jar",
"C:\\Users\\hagsig\\AppData\\Roaming\\BurpSuite\\mcp-proxy\\mcp-proxy-all.jar",
"--sse-url",
"http://127.0.0.1:9876"
]
},
"nmap": {
"command": "python",
"args": [
"C:\\Users\\hagsig\\nmap-mcp-server\\nmap-mcp-server.py"
],
"env": {
"PYTHONUNBUFFERED": "1"
}
}
}
}
4. 클로드와 Nmap MCP 서버 연동 확인
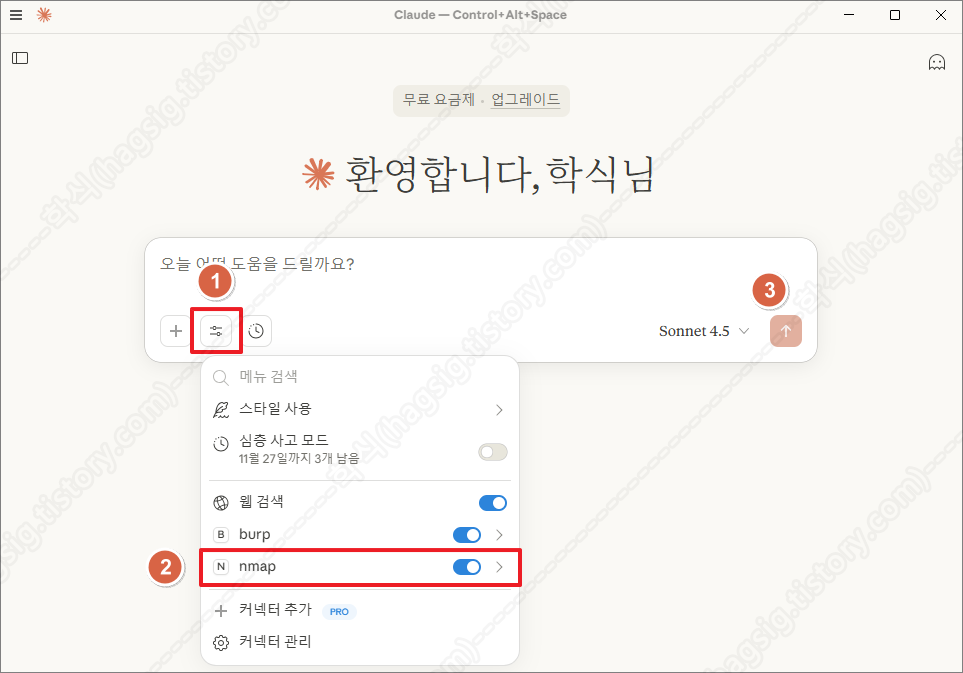
- 클로드를 종료하고 재 실행한 뒤, 아래의 사진과 같이 사용자 프롬프트에 nmap이라는 옵션이 생겼는지 확인한다.
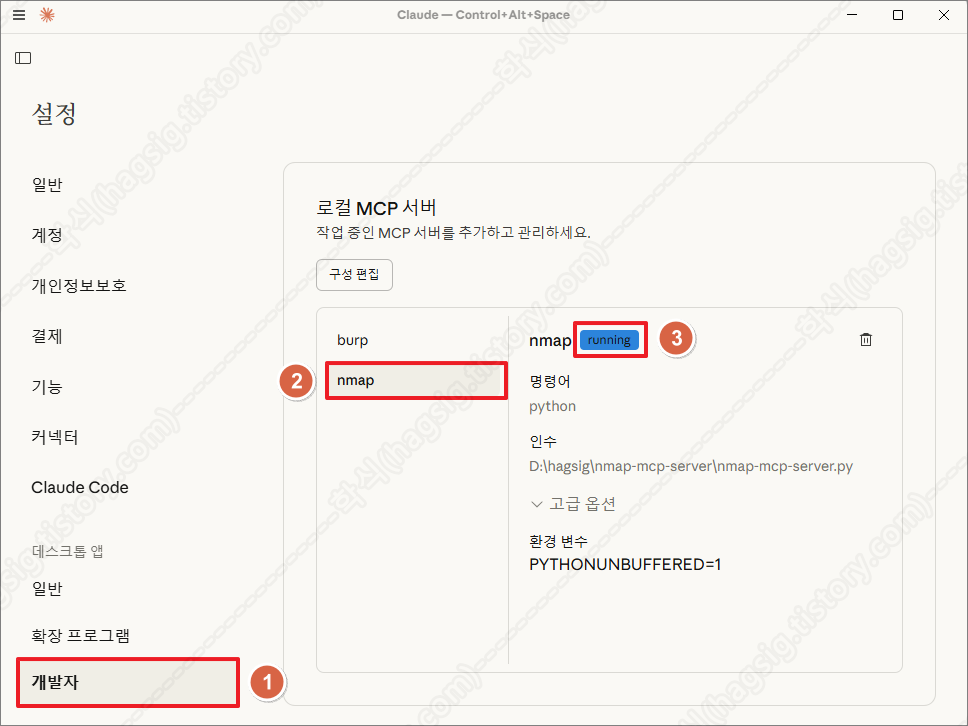
- 설정의 개발자 메뉴에서 아래의 사진과 같이 running이라고 표시되는지 확인한다.
- 위 두 가지가 모두 확인된다면 Nmap MCP Server가 정상 동작하고 있고, 클로드와 연동이 성공한 것이다.
다. AI 네트워크 스캔 수행
1. 점검 옵션
- 현재는 아래의 사진과 같이 nmap-mcp-server.py 파일에 작성한 5가지의 기능만 제공하고 있다.
- 추가적으로 원하는 기능은 클로드에 물어보고, 답변받은 소스코드를 nmap-mcp-server.py 파일에 추가하면 된다.
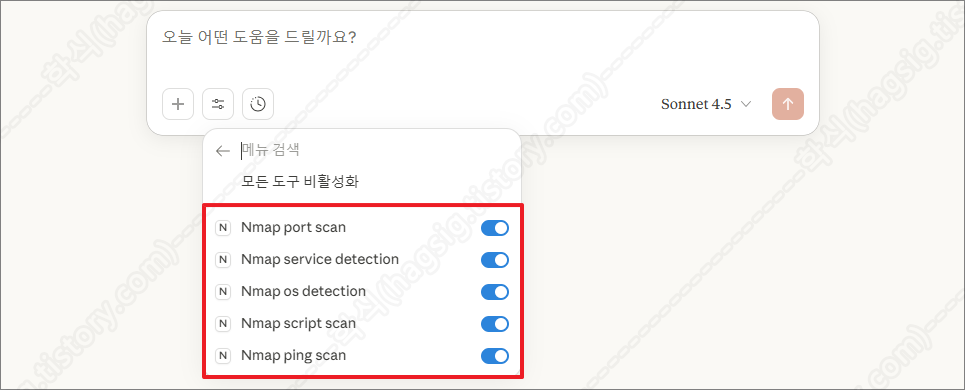
- 클로드 Nmap 옵션(도구)
| 옵션(도구) | 설명 |
| Nmap port scan | 대상 호스트에서 열려있는 네트워크 포트를 찾아내는 기본적인 스캔한다. |
| Nmap service detection | 열려있는 포트에서 실행 중인 서비스의 상세 정보를 파악한다. |
| Nmap OS detection | 대상 시스템의 운영체제를 식별한다. |
| Nmap script scan | NSE(Nmap Scripting Engine)를 사용하여 고급 탐지 및 취약점 스캔을 수행한다. |
| Nmap ping scan | 대상 호스트가 살아있는지(온라인 상태인지) 확인하기위해 가볍게 스캔한다. |
2. 점검 예시
- 클로드에 아래의 프롬프트를 입력하여 Nmap을 이용한 네트워크 스캔을 수행할 수 있다.
예시 1: "192.168.1.1의 열린 포트를 스캔해 줘"
예시 2: "10.0.0.5에서 실행 중인 서비스 버전을 확인해 줘"
예시 3: "192.168.1.0/24 네트워크에서 활성화된 호스트를 찾아줘"
예시 4: "example.com의 80, 443 포트에 대해 http 관련 NSE 스크립트를 실행해 줘"
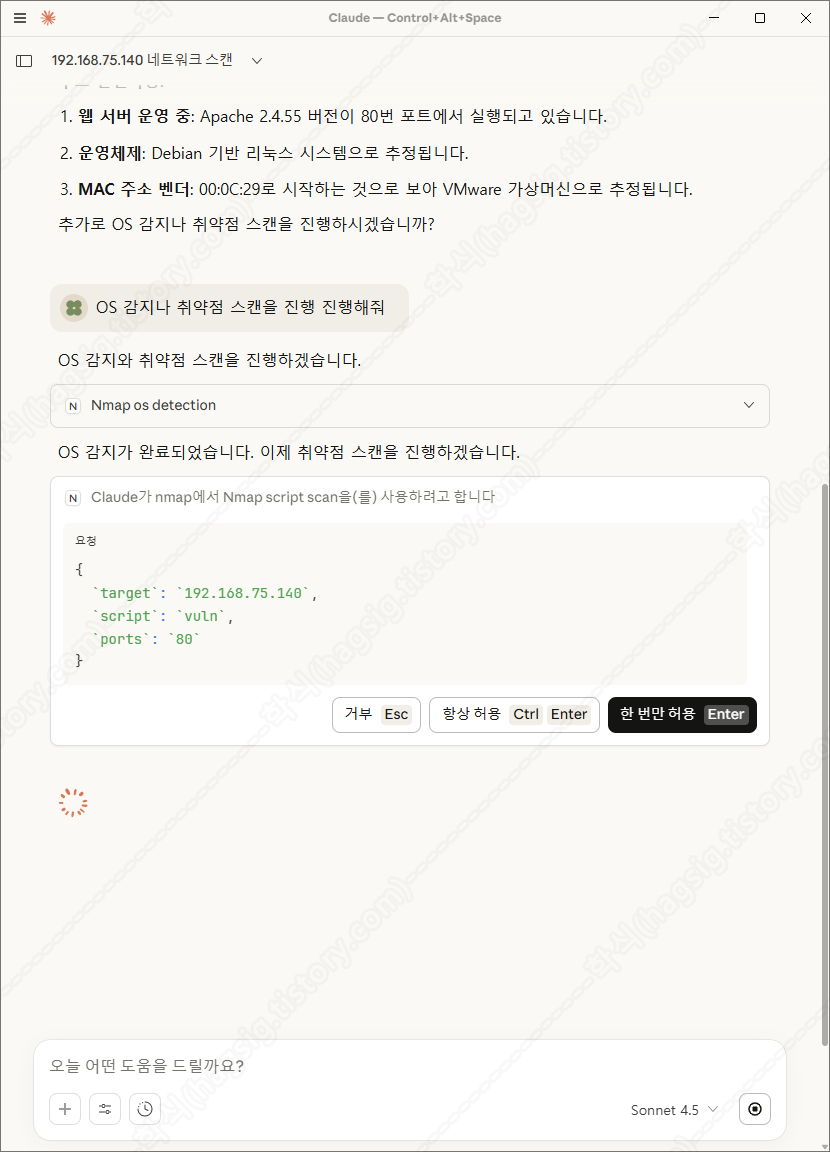
- 아래는 테스트환경에 네트워크 스캔을 지시하였을 때의 동작과정 및 응답이다.
- 각 과정별로 사용자에게 동의를 구하고 작업을 수행하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
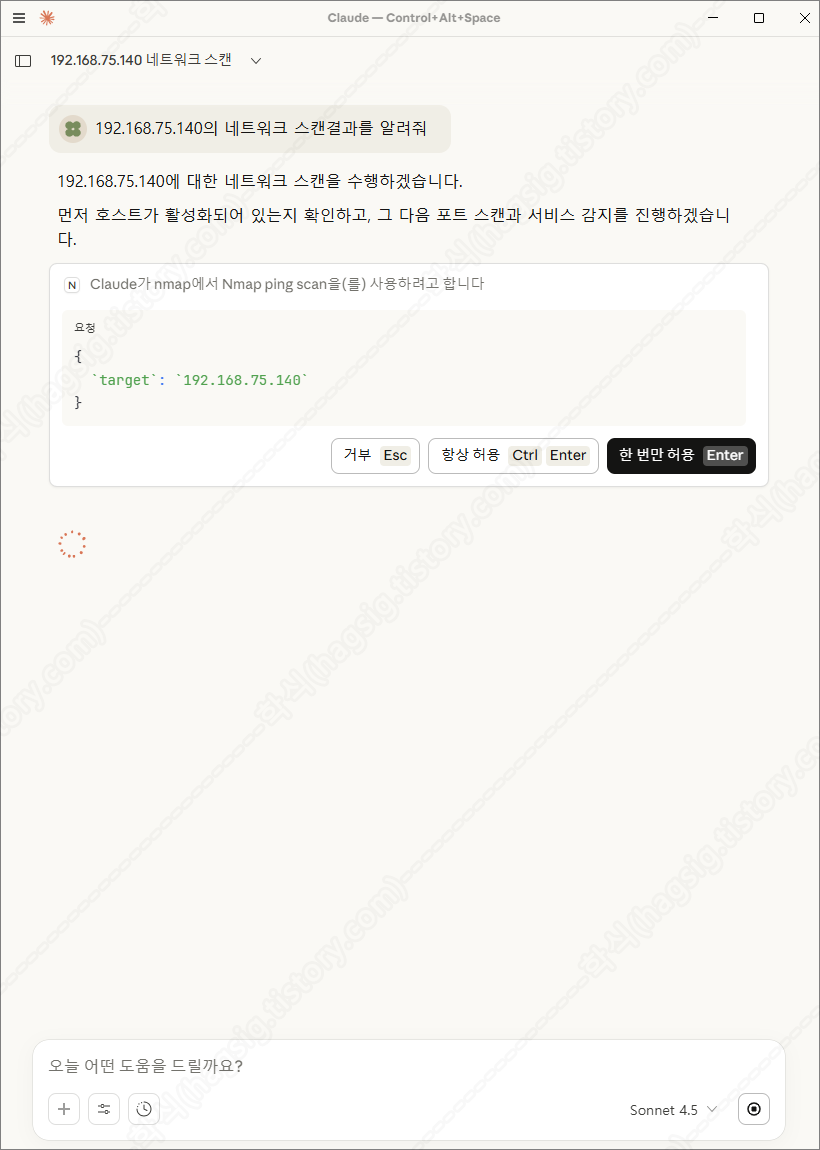
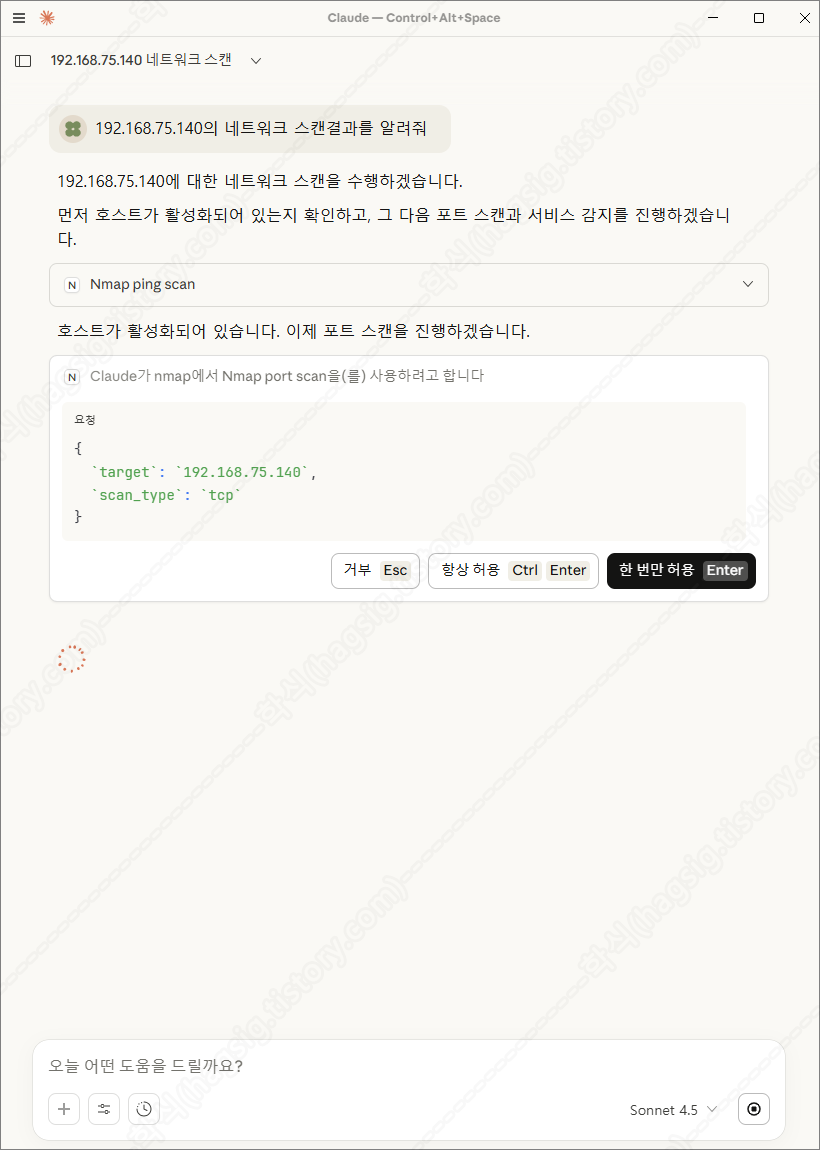
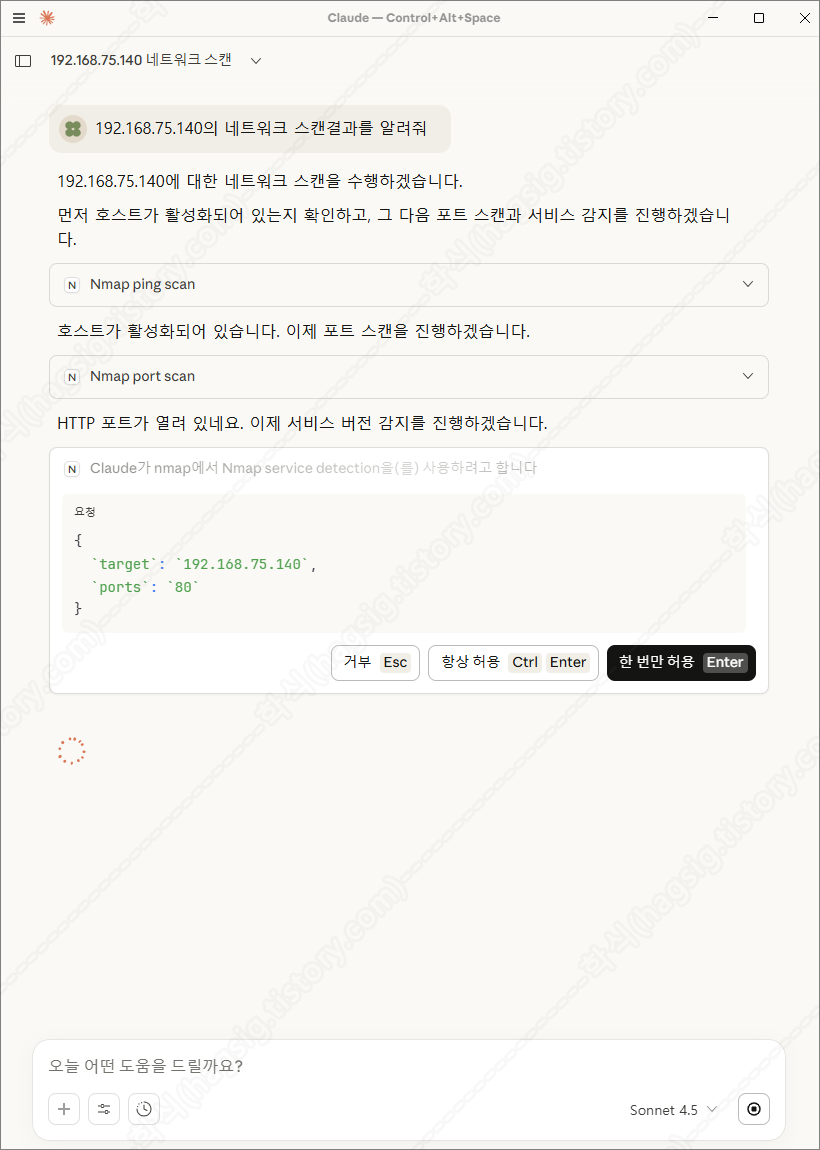
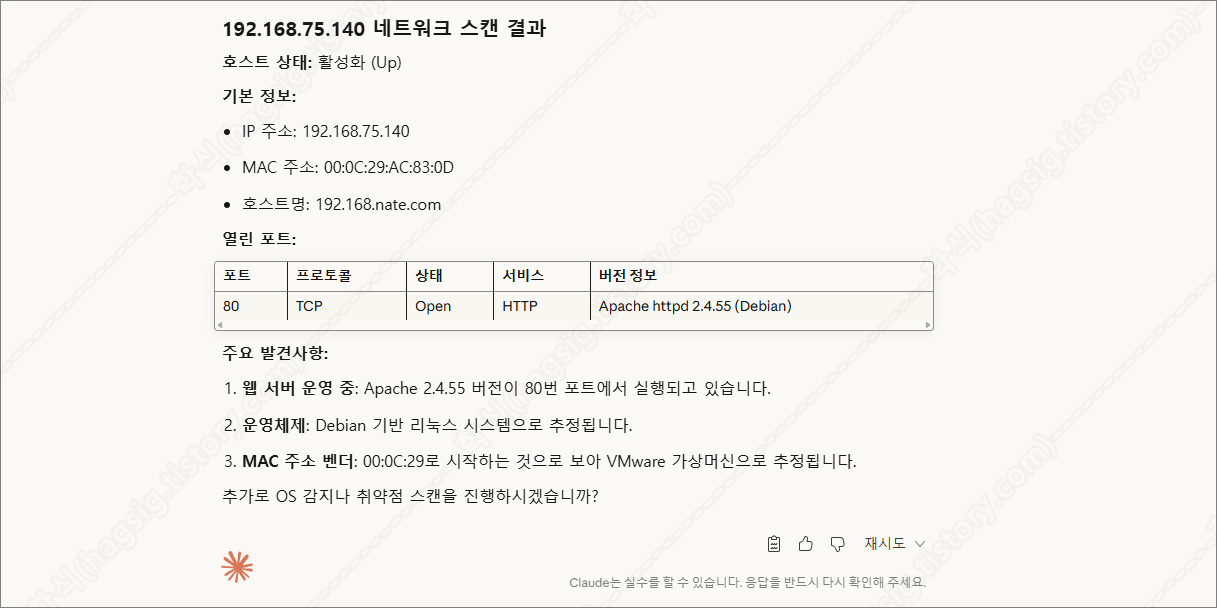
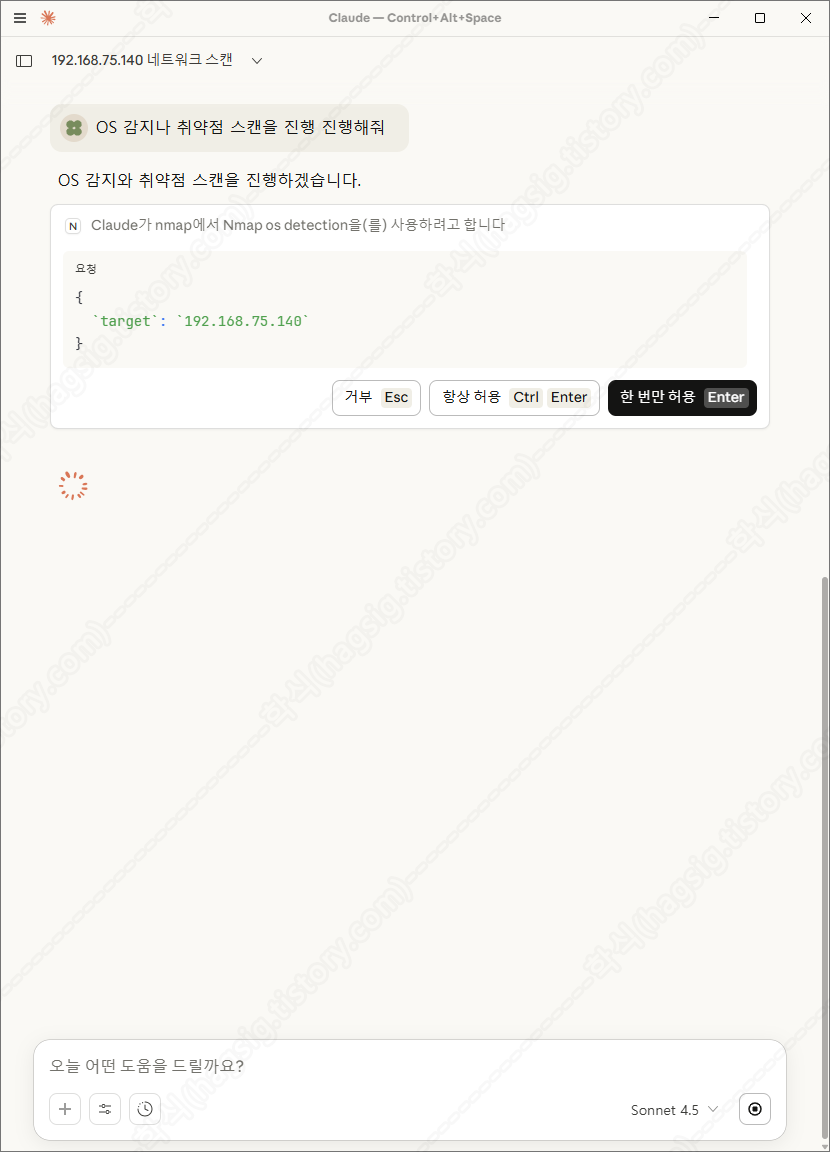
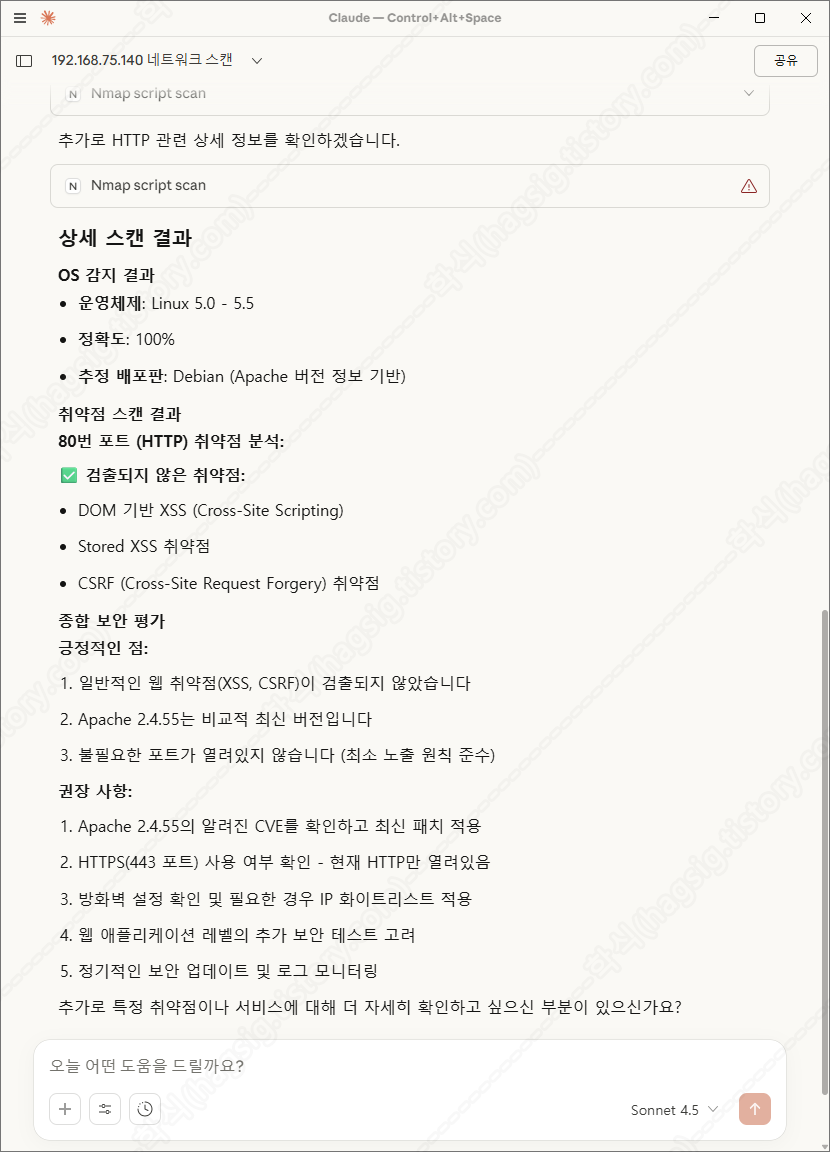
- 스캔 후 취약점을 찾아달라고 하면 아래와 같은 과정을 통해 취약점을 찾아준다.
'AI 취약점진단 · 모의해킹' 카테고리의 다른 글
| AI를 활용한 SQL Injection 공격 방법(SQLMap+Claude+MCP) (0) | 2025.11.21 |
|---|---|
| AI를 활용한 하위 디렉터리/서브도메인 스캔(Gobuster+Claude+MCP) (0) | 2025.11.21 |
| AI를 이용한 웹 모의해킹 방법(BurpSuite+Claude+MCP) (0) | 2025.11.18 |
| '25 OWASP LLM03: Supply Chain 공격 유형 (0) | 2025.11.11 |
| '25 OWASP LLM02: Sensitive Information Disclosure 공격 유형 (0) | 2025.11.08 |